Dialysis
There are two main types of dialysis:
If you are interested to know more about the treatment options, please watch this video.
Peritoneal dialysis (PD / Water dialysis)
Features
- A daily home-based treatment.
- Can be done by yourself or your caregivers.
Getting started
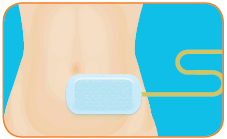
This picture shows the access point and catheter required for Peritoneal Dialysis (PD).
- You will need a minor surgery at your belly to create an access point.
- A small, soft plastic tube called a catheter will be inserted through this access point.
- You will spend at least one night in the hospital for this surgery.
- A nurse will teach you or your caregiver how to do PD.
Treatment process
- Cleansing fluid flows into your body and removes toxins through the catheter.
- This exchange happens a few times to reduce the toxin levels in your blood.
- Can be done manually or by a machine.
Logistics
- Need space to store the machine and water bags for PD.
- Need to keep the machine and house clean to avoid infection.
There are two types of PD in Singapore:
- Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) where the exchange is done manually.
- Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD) where the exchange is done by a machine.
A. Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD)
- Done manually at home.
- Done on a daily basis.
- 3 to 5 times a day, with each exchange taking 20 to 30 minutes.
- Patients can usually continue with normal daily activities between exchanges.
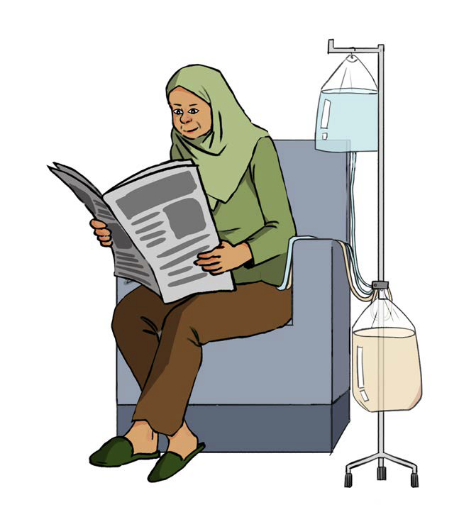

This picture shows a woman undergoing Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) at home.
B. Automated peritoneal dialysis (APD)
- Done by a machine at home.
- Done on a daily basis.
- Once a day, for 8 to 10 hours, typically during sleep.
- Patients can usually continue with normal activities during the day.
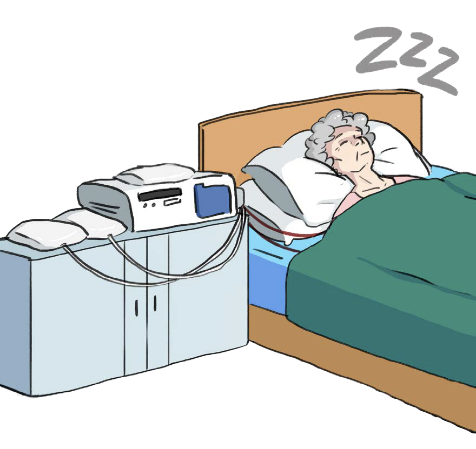
This picture shows a woman undergoing Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD) at night during her sleep.
Key factors to consider for PD
- Requires a minor surgery before starting dialysis
- Daily treatment
- Done at home
- You or your caregivers need to learn how to do PD
- Requires space at home for PD machine and water bags
- Can be done when it is convenient for you
- Your sleep may be disturbed if you do APD during sleep; your day will be free if you do APD during sleep
- Less strict diet and fluid intake than HD
- Risk of infection
- On average, less expensive than HD
- You need to bring PD equipment when you travel abroad
Hemodialysis (HD / Blood dialysis)
Features
- Usually done at a dialysis centre in Singapore.
- About 3 times a week.
- Each session takes around 4-6 hours.
- Most patients can go on with normal daily life when not receiving dialysis.

This picture shows the access point required for Hemodialysis (HD).
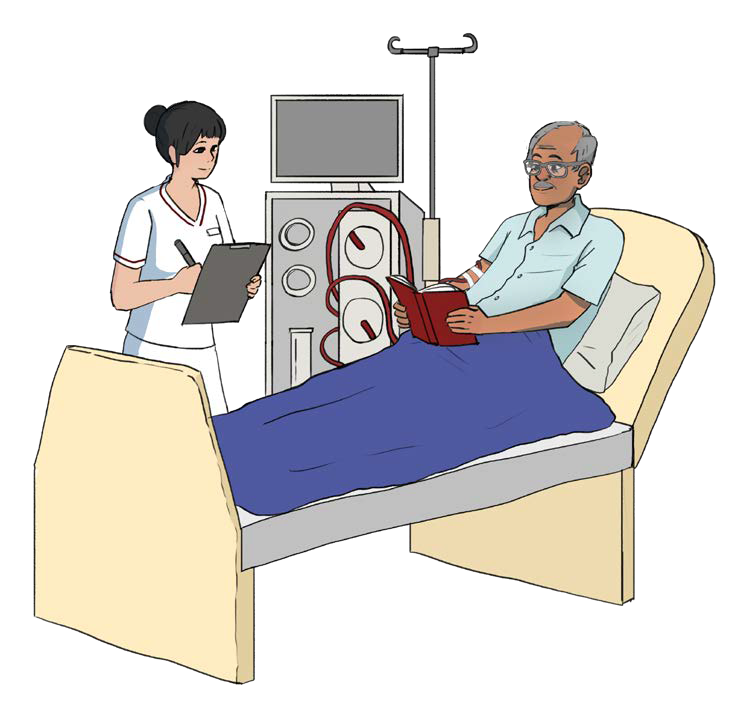
This picture shows a man undergoing Hemodialysis (HD) at a dialysis centre.
Getting started
- You will need a minor surgery at your arm to create access to your blood.
- However, the blood vessel needs 2-3 months after the surgery to be
ready for dialysis.
- During this time, you can receive HD via a temporary access point
through a plastic tube around your neck or chest.
Treatment process
- Every time you receive HD, needles will be placed in your arm.
- An artificial dialysis filter in the HD machine will clean your blood.
Logistics
- You will need to travel to a dialysis centre to get HD.
- There are centres all over Singapore. A healthcare provider can connect you with a suitable dialysis centre.
Key factors to consider for HD
- Requires a minor surgery before starting dialysis
- About 3 sessions per week, 4 - 6 hours per session
- Have to travel to and from dialysis centre
- Nurses at the dialysis centre will perform dialysis for you
- Chance of meeting other patients at dialysis centre
- Needles will be used every time you get dialysis
- May feel tired after a dialysis session
- Stricter diet and fluid intake compared to PD
- Risk of infection
- On average, more expensive than PD
- You need to arrange with a dialysis centre when you travel abroad